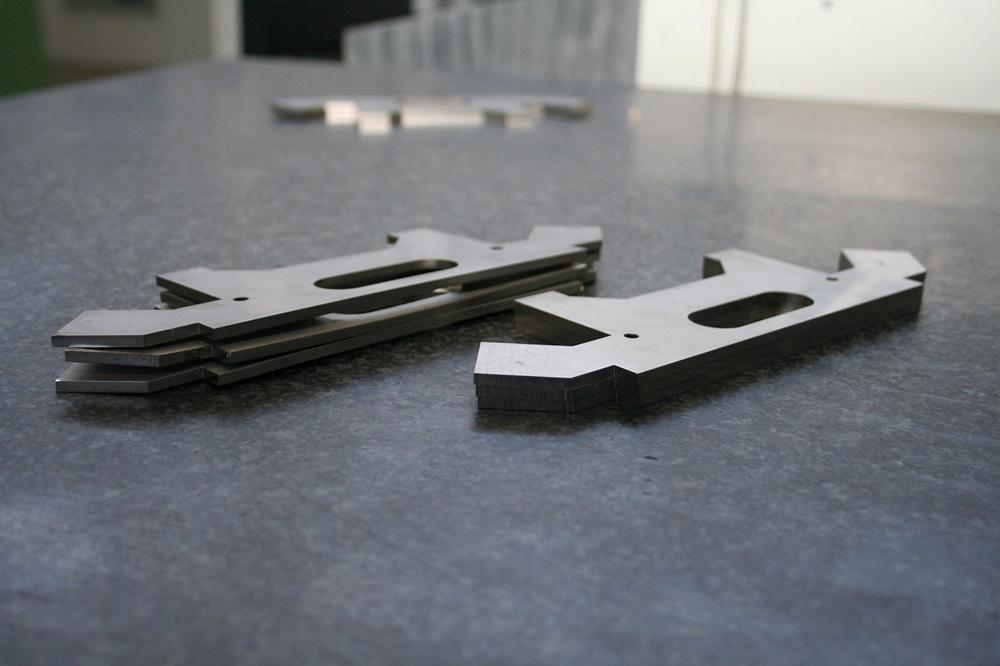
Distorted laser-cut elements (left) can wreak havoc on downstream operations.
Let’s not beat throughout the bush proper right here: Throughout the sheet metallic and plate fabrication world, leveling is a course of all people likes to hate. Fabricators in any case want to acquire laser-flat sheets which may be decrease into burr-free, dead-flat elements that head correct to the following downstream course of. That’s the perfect, nevertheless we don’t keep in a extremely good world. Every movement has a response. In case you work supplies, you modify its stress traits. It’s physics.
Leveling is often appeared upon as a non-value-adding course of. In actuality, though, when you check out your total metallic fabrication value stream, along with downstream processes like bending and (notably) welding, you see merely how lots value a well-tuned leveling operation offers. Jobs stream with out problem—no struggles fixturing distorted elements, no frustratingly prolonged setups on the press brake, no paint safety factors as a consequence of poor upstream processing. Sending a pile of warped blanks down the price stream is like throwing a jagged rock into calm waters. The ripple outcomes run far and broad.
Wherever it happens—sooner than thermal slicing (sheet leveling) or after (half leveling)—the strategy stays a vital step inside the metallic fabrication value chain. Used accurately and precisely, it might enhance prime quality, straightforward half stream, and, in the long run, make a metallic fabricator further aggressive.
Deal with Your (Supplies) Stress
No experience can take away all residual stress from sheet metallic or plate, though the newest leveling strategies get very shut. The idea is to remove as lots residual stress as you probably can so that the metallic behaves predictably downstream. Moreover discover that manually manipulating elements after slicing—say, with a roll bender or totally different system—once more to a flat state does not relieve the interior stress. Such handbook, uncontrolled cold-working can in precise reality induce further stress into certain areas and, due to this fact, wreak havoc on downstream processes.
Warping factors might be obvious, notably for fabricators manufacturing precision merchandise to a specified, very tight flatness tolerance. Many cases, however, the difficulty isn’t so obvious. Reduce elements look flat as soon as they’re stacked. However downstream, the welding division supervisor struggles with a robotic educate pendant. Try as he may, he can’t get the robotic to create a top quality weld. The fit-up merely isn’t fixed, and that’s as a consequence of extreme interior stresses all through the elements that showcase all through welding.
You dig a bit deeper. It appears, your handbook welders knew this weldment launched factors. They’d regulate their technique and tweak the fixturing to “make it work.” Merely part of the job, they thought.
Just because a part is flat doesn’t indicate it’s stress free. As welders apply heat, the stress manifests itself as a result of the workpiece begins to bow. Rework ensues—further clamps, tweaked welding method, new clamp placement, further tweaking. Quite a bit for trying to automate.
The Fundamentals of Roller Leveling
Roller leveling stays the most common technique to remove residual stress from sheet and plate. It’s confirmed and simple. Greater and reduce leveling rolls, with backup rollers behind them, are set with a distinct segment in between them. The outlet on the entry rolls begins at a share (typically spherical 50%) of the material thickness, then ends up equal to the material thickness on the exit rolls (see Decide 1).
Stress from the rolls repeatedly brings the material earlier its yield stage as the material serpentines by the use of the machine. The material then is straightened and labored a lot much less and fewer as a result of it approaches the exit rolls. The underside rolls keep stationary whereas the best roll-set tilts to create the rising roll gap between the entry and exit rolls. The sturdy bends on the entry rolls take away that residual stress, whereas the rolls near the exit return the material to a flat state. The material that emerges not solely is visibly flat however as well as has most of its residual stress eradicated. (As soon as extra, discover the phrase “most.” Leveling can take away virtually all residual stress, nevertheless it doesn’t take away all of it.)
Troublesome leveling work, like functions involving high-strength supplies, can title for explicit leveler designs. In a number of circumstances, a six-high leveler typically is an effective choice (see Decide 2). These have three rows of rolls above and beneath the workpiece: the assistance rolls, the intermediate rolls, and the leveling rolls that contact the workpiece. Specialty strategies have motorized, adjustable “backups” beneath the leveling rollers that apply pressure specifically areas of the work—say, to remove edge wave on the edges of a sheet (see Decide 3).
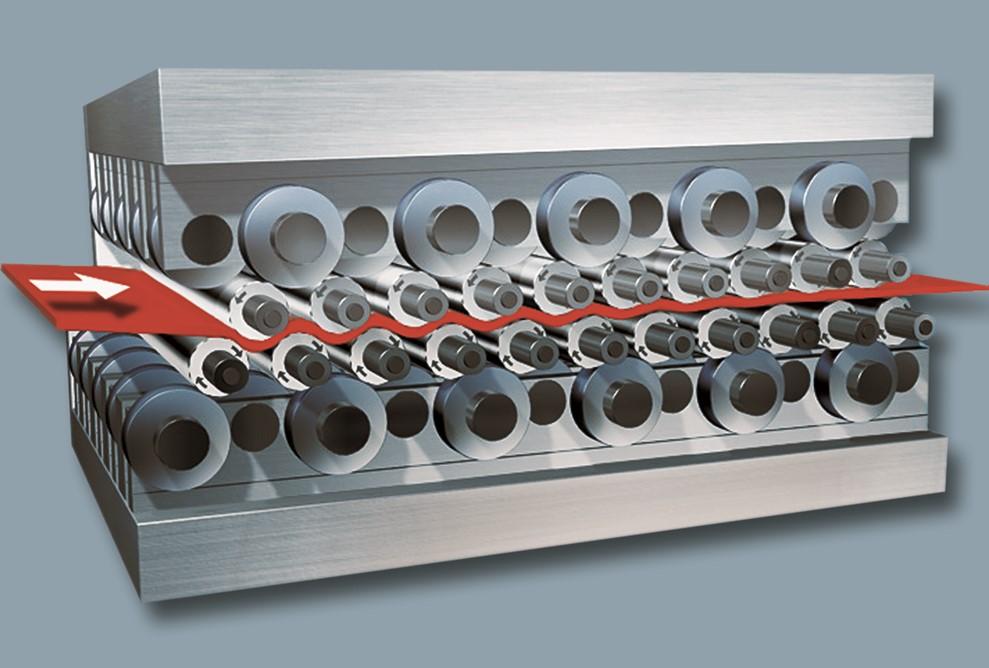

FIGURE 1. A roller leveler bends the material earlier its yield stage, then straightens it as soon as extra to flat as a result of it approaches the exit rolls.
The alternatives abound, nevertheless the intention stays straightforward: to take care of defects like edge wave, center buckle and coil set, and, arguably most important, the residual stress. For some defects like edge wave or center buckle, roller levelers use adjustable backup rollers to precisely apply further pressure onto the material at explicit spots. This allows the leveling rollers to deflect specifically areas all through the sheet, addressing defects like edge wave and center buckle. Some machines moreover tilt the upper rollers in such a way that eliminates explicit type defects (see Decide 4).
Important Parts
Choosing a leveler requires specializing in three principal supplies elements: the thickness range, yield power, and flatness tolerances. Two grades is maybe the equivalent thickness, however when their yield components are dramatically fully totally different, they might have fully totally different gap settings on a leveler.
Cutouts are one different situation. Two provides is maybe the equivalent grade with the equivalent specified yield stage and even the equivalent thickness, however one has cutouts and the alternative would not. Check out elements will seemingly current the material with cutouts behaves otherwise.
Heat treatment might enter the equation. If decrease blanks bear heat treating after which require leveling, letting these scorching blanks cool completely is maybe a difficulty. The material yield rises after cooling. Usually it’s so laborious and brittle that the leveler induces cracking and will most likely break the elements.
To forestall this, operators in certain circumstances choose to heat-treat after which, as a result of the blanks are cooling and nonetheless malleable, ship them by the use of the leveler, after which they let the elements cool completely. This isn’t widespread mainly fabrication, nevertheless for certain sectors, like knife and observed blade manufacturing, the approach works terribly successfully.
Supplies Grades, Ground Scenario, and Burrs
Stainless steel and aluminum might be considerably inclined to warping, nevertheless it might happen to any supplies, along with thick carbon metallic. A fabricator may get what seems to be fully flat carbon metallic plate from the mill, but it surely discovers the material distorts when processed downstream. The plate is maybe flat, nevertheless the residual stress continues to be hiding inside. So, it sends the plate by the use of a high-quality leveler, after which the objects stream downstream with out problem.
Ground conditions can even situation into the equation, counting on the fabrication requirements. In some circumstances, operators ship hot-rolled plate by the use of the leveling machine, scale and all. The rollers themselves are hardened, so that they aren’t affected by scale and particles. That talked about, they do must be cleaned, notably if a retailer produces surface-critical elements along with scaly carbon metallic. In a number of circumstances, operators may run scaly hot-rolled inside the morning, pull out the roller cassettes to clean the precept and backup rollers, then run surface-critical supplies inside the afternoon.
The equivalent would apply for hot-rolled pickled and oiled (HRP&O) or one other supplies with an oily flooring. Positive, that oil does get on the rollers, nevertheless as long as the leveler cassettes are cleaned often, the machine should operate with out problem. The oil doesn’t affect machine operation the least bit. Operators merely wish to wash the rolls to verify oil isn’t transferred onto totally different elements.
Blasted surfaces moreover have an effect, though plenty of the factors emerge indirectly—by the use of burrs. Slicing these blasted surfaces, considerably with a laser, can create some important dross that requires deburring, and other people burrs might be problematic for a leveler. The leveler works as supposed, nevertheless it could actually additionally “press” these burrs onto the plate edges. This makes a poor edge even worse and, if unaddressed, might trigger factors downstream, notably if the sting will most likely be painted. To rectify it, an operator should not solely grind it however as well as perform some edge rounding—a feat that takes time and ending experience.
Burrs mainly can create points, which is why deburring and half leveling are typically used as complementary processes. Say a slicing course of creates a extremely small burr. It would drop off neatly after the leveler’s rolls make contact, nevertheless that’s not assured to happen. The burr may embed itself into the sting. And tiny as that burr is maybe, it nonetheless can stick out like a sore thumb after painting.
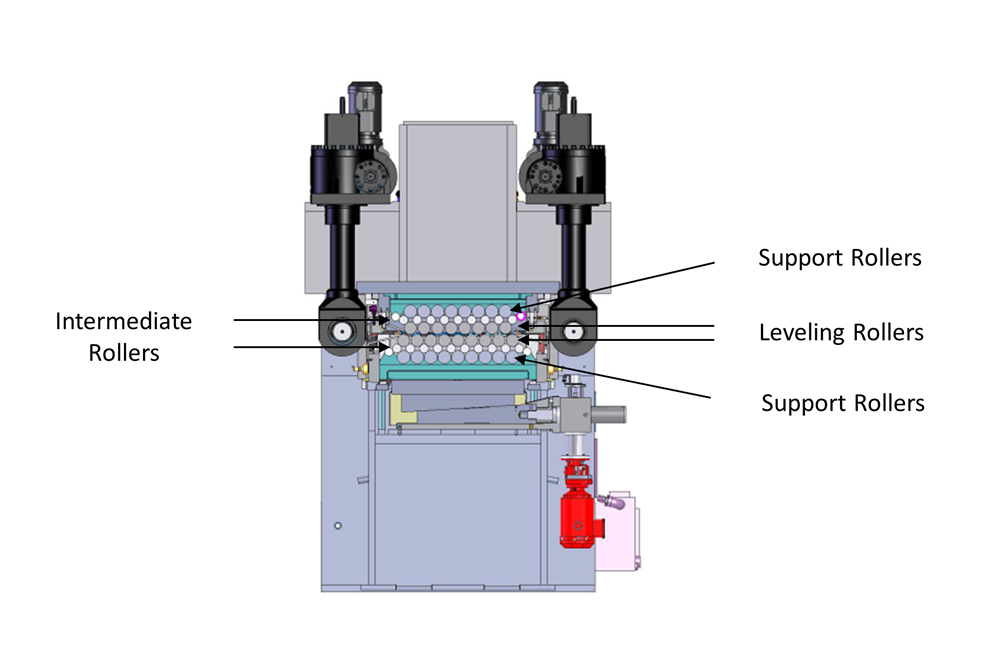
FIGURE 2. A six-high roller design has assist, intermediate, and leveling rollers above and beneath the material being leveled.
One of the best technique is to cut first, then deburr, then diploma, then put collectively the ground for painting (by the use of blasting or cleaning and pretreatment). Even so, this course of order will not be doable for elements which may be distorted. A deburring machine is simply not a part leveling machine. Its brushes work successfully when dealing with barely and even moderately warped elements. Nevertheless they aren’t designed to deburr severely warped supplies. At best, the brushes will grind intently in some areas nevertheless go away totally different areas untouched. In these circumstances, a fabricator might have no choice nevertheless to diploma that severely distorted workpiece first.
Ideally, a fabricator can scrutinize the leveling that occurs sooner than slicing, so the half doesn’t distort so severely on the slicing desk inside the first place, along with the slicing course of itself, along with the slicing parameters, toolpath sequence, and basic nesting approach. In the end, a bowed half will enhance the likelihood for head crashes and makes the primary slicing course of a lot much less predictable basic (see Decide 5).
Sizing a Leveler
Investing in a leveler isn’t like investing in, say, a press brake or laser slicing machine. A high-product-mix job retailer may choose the most important slicing desk, the perfect fiber laser slicing power, and the longest brake mattress it might afford to take care of the most important variety of elements, every in dimension and thickness.
Leveling doesn’t work like that. Proper this second’s strongest machines can diploma supplies that’s larger than 2 in. thick. Nonetheless, these machines won’t be designed to take care of the entire range of cloth thicknesses and yield strengths.
Roll diameter and the spacing between them are all designed to take care of a selected thickness range. For individuals who try and diploma very skinny sheet on a roller leveler designed for thick plate, the pitch between the rolls will most likely be too big to diploma and take away that residual stress accurately. Conversely, for individuals who try and diploma thick plate on a roller diploma designed for skinny sheet—with small roll diameters pitched fastidiously collectively—the machine gained’t work as supposed, and you might end up damaging the material.
The easiest technique is to determine on a leveler that matches most of your product mix. You then can depend upon exterior service suppliers for the remaining. This in any case comes with a worth, nevertheless relying in your supplies present state of affairs, it’s maybe the only option.
Half Geometry Parts
There’s no getting spherical the reality {that a} fabricator’s main slicing operation induces stress, and every the decrease path and half geometry play a activity in how that stress makes itself recognized on the slicing desk.
Prolonged elements are considerably inclined to distortion, as are elements with big cutouts. Counting on the experience, thermal slicing all these cutouts can put a great deal of heat into the material—an environment ripe for further distortion and further interior stress.
Levelers can even have factors with microtabs holding various elements or interior cutouts in a decrease sheet. Leaving cutouts in place inside a laser-cut half is maybe an excellent decision for supplies integrity when, say, you’re bending a giant workpiece on a press brake; in the end, big, skinny workpieces with big cutouts might be troublesome to take care of. Nevertheless partly leveling, these microtabs can sometimes break as rollers ship the material earlier its yield stage.
Spherical elements present distinctive challenges. For spherical elements that must be fully flat, an operator sometimes sends the piece by the use of a part leveler as quickly as, then rotates it by 90 ranges and sends it by the use of as soon as extra. This eliminates distortion in every directions and creates a dead-flat clear. Leveling circles twice does take a while—nevertheless as soon as extra, doing so can take away so many problems downstream.
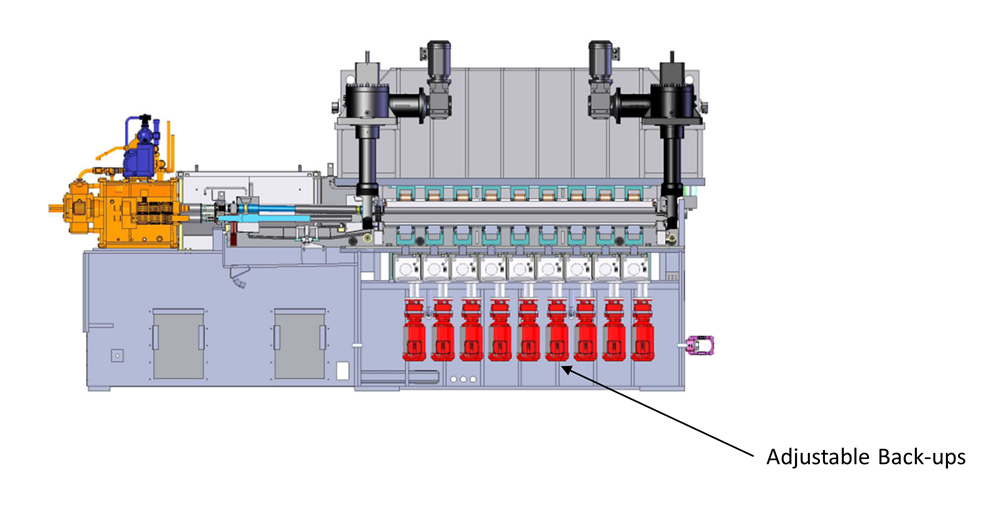
FIGURE 3. Some roller levelers have adjustable backups that apply pressure specifically areas, correcting for type defects.
Leveling in Context
To drive basic costs down and make your manufacturing operation predictable, residual stress low cost ought to happen someplace inside the present chain. If low-cost supplies hasn’t been leveled accurately, its true worth typically is lots elevated.
As a course of, leveling have to be put in context. Take into consideration you have gotten sheet throughout which solely 30% of the residual stress has been eradicated sooner than laser slicing. Which implies you have gotten 70% of stress remaining. Laser slicing offers one different 20%, making a aggravating state of affairs (so to speak) even worse.
How lots leveling is required depends on the equipment. Some operations—notably these that focus on high-precision work like aerospace and medical—might have sheet leveling sooner than laser slicing and half leveling after. As soon as extra, it depends on flatness requirements and the best way supplies stress impacts downstream operations.
Regardless, the upper these blanks are prepared for downstream processing, the additional predictable your total metallic fabrication value stream might be. Gadgets are deburred and edges are rounded after which leveled to a super flatness. That gives a level of precision the place even extraordinarily automated downstream processes can thrive.
